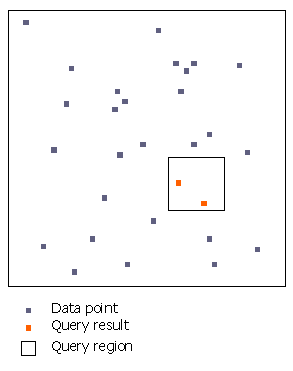
 One space contains a set of 2-dimensional
points. This set of points is large and dynamic, so the data set is
stored in a B-tree on disk. The query region is a single, box-shaped
object. Because this data set contains a small amount of static data,
(just one box), it makes sense to use a sorted array as the underlying
data structure. Geophile combines these two spaces using spatial join
to find the points inside the query region. Geophile can also be used
to cluster the points on disk, to minimize the number of disk accesses
required by the search.
One space contains a set of 2-dimensional
points. This set of points is large and dynamic, so the data set is
stored in a B-tree on disk. The query region is a single, box-shaped
object. Because this data set contains a small amount of static data,
(just one box), it makes sense to use a sorted array as the underlying
data structure. Geophile combines these two spaces using spatial join
to find the points inside the query region. Geophile can also be used
to cluster the points on disk, to minimize the number of disk accesses
required by the search.