The choice of a data structure is dictated by the characteristics of the data set. Sorted arrays work well for static, memory-resident data sets. Balanced binary trees and skiplists work well for dynamic, memory-resident data sets. B-trees are best suited for large, dynamic disk-resident data sets.
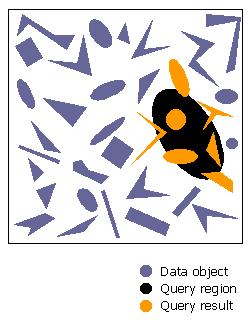 Many applications need
data structures which support spatial searches. For example, a
geographic application might store a set of landmarks, and retrieve
all landmarks inside a query region. A mechanical CAD application
might need to detect interference among 3-dimensional objects. In both
cases, the data items to be stored are spatial objects, and the
selection criterion is not equality or membership in a range, but
spatial containment or overlap.
Many applications need
data structures which support spatial searches. For example, a
geographic application might store a set of landmarks, and retrieve
all landmarks inside a query region. A mechanical CAD application
might need to detect interference among 3-dimensional objects. In both
cases, the data items to be stored are spatial objects, and the
selection criterion is not equality or membership in a range, but
spatial containment or overlap.